קורס בינה מלאכותית : RB20 – שיעור 3 Time series ולמידת מכונה
יצירת VIRTUAL ENV

הרצת ה ENV
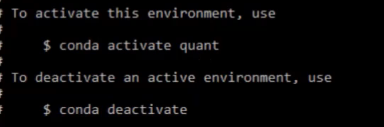
conda create –name env_image1 python=3.5.4
conda activate env_image1
conda info –envs
למשל
D:\TWS API\source\pythonclient
הסדרות אינם מציטות ל GUASS-MRKOV בניגוד למידע ריגרסיה ליניארי
index2018.csv ייש להורדי

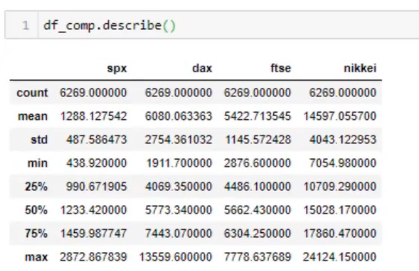
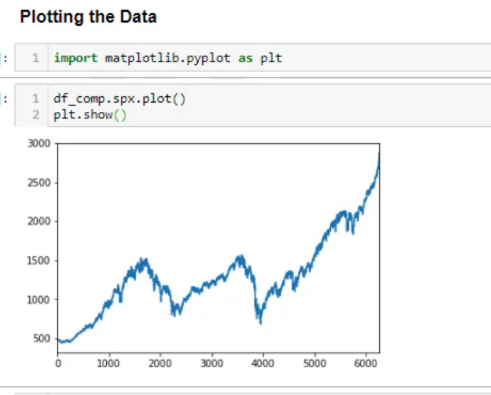
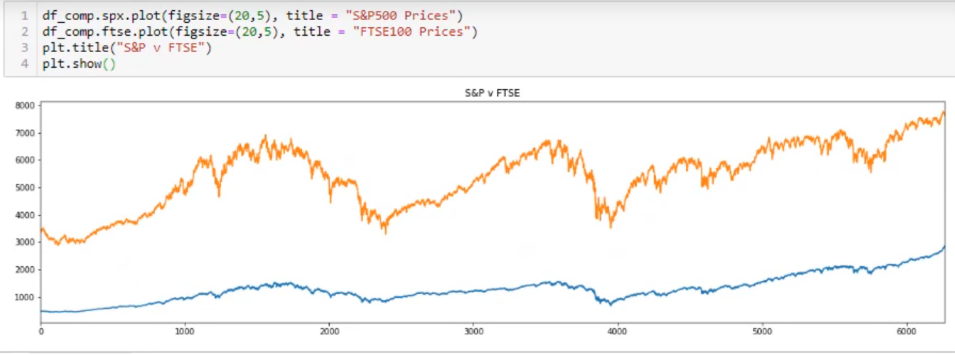
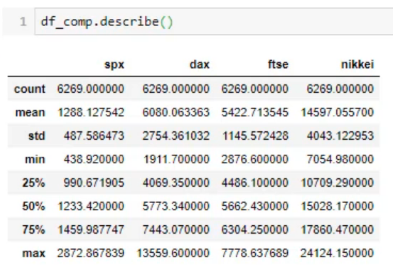
נבדוק בצורה ראשונית את הנתונים

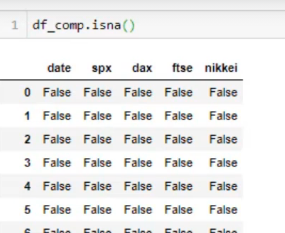
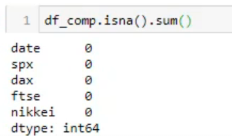
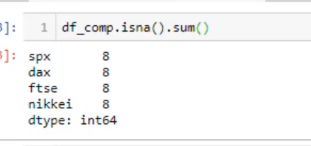
נריץ בדיקה איפה חסר נתונים :
פניה ישירה לעמודה
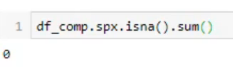
הדפסת הערכים
קרולציות בין שתי סדרות זמן
QQ PLOT


ציך ה Y מראה ערך למשל מחיר מ 0 עד 3000
ציר ה X מראה את כמות הפיזור – יש לבדוק לעומק התפלגות זאת
DATE
נמיר את הזמן מצב טקסט למצב תאריך
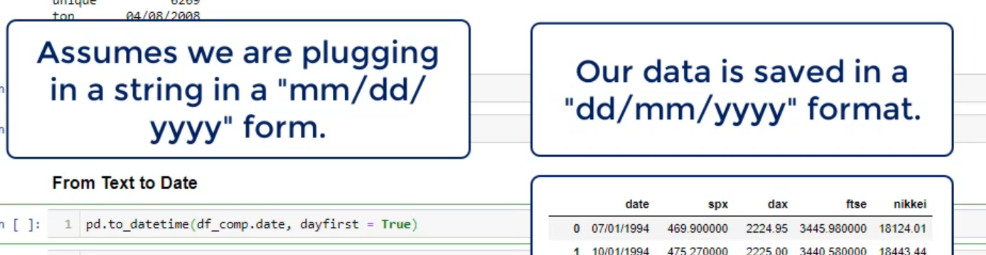
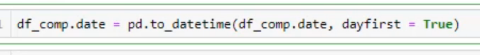
נכניס לתוך משתנה
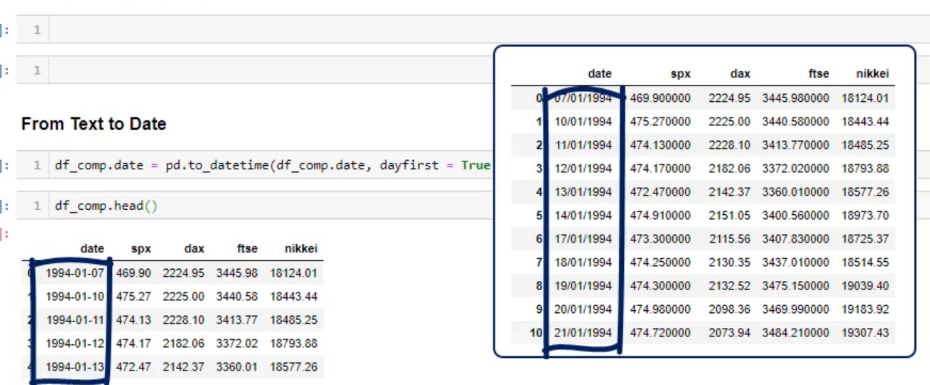
עכשיו נקבל מידע בצורה טובה – שנוכל לבצע ניתוח
יצרית אינדקס DATE

בגלל שהם אינדקס



re kph hnh gcsuv
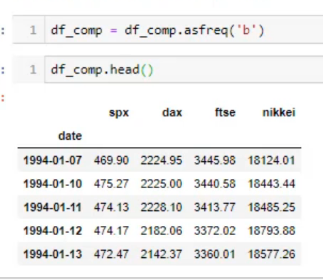

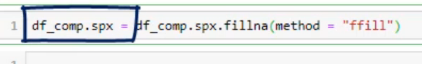
ממלאים תאים חסרים לפי תא לפני או תא אחרי ועוד
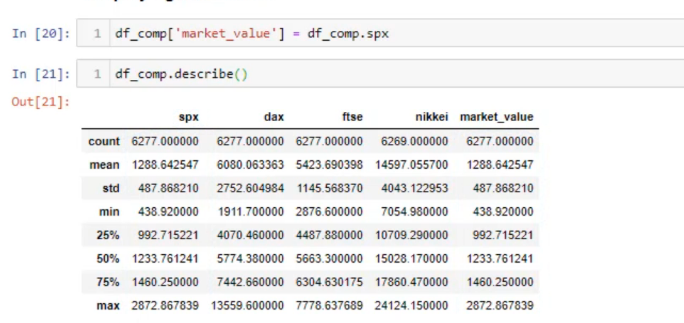
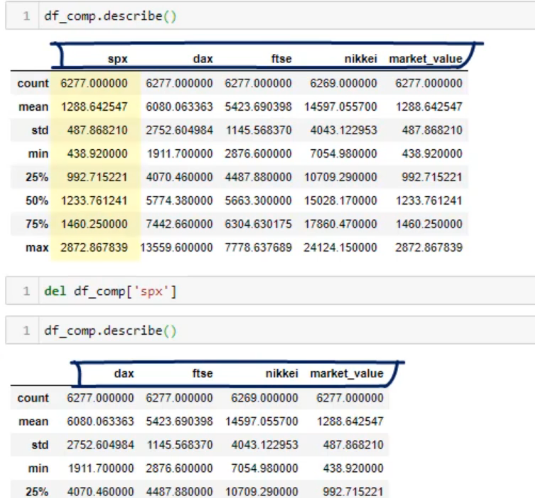
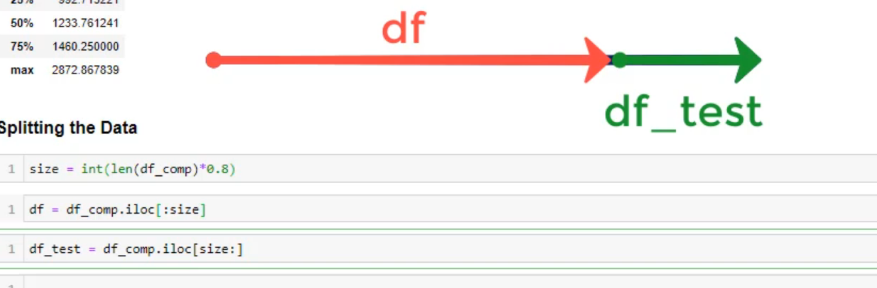
פיצול דאטא פריים עבור למידת מכונה
![]()
בדיקה שאין OVER LAPPING

ניצור רעש לבן על DATAFRAME קיים

![]()
על מנת להשוות סדרות צריך שיהיה להם אותו אורך ואותו גובה
רעש לבן

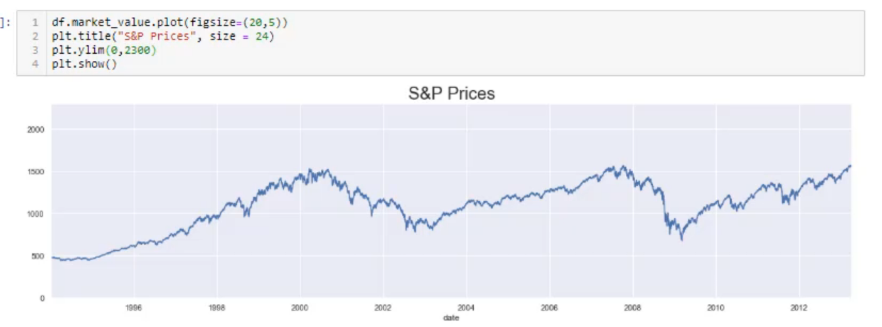
,
Stationarity
here are some examples of stationary and non-stationary time series:
- Stationary Time Series:
An example of a stationary time series is a series of annual rainfall measurements over many years in a region where the climate remains relatively constant. In this case, the mean, variance, and autocovariance of the rainfall measurements remain constant over time.
- Non-Stationary Time Series:
An example of a non-stationary time series is a series of monthly temperature measurements over many years in a region that experiences seasonal changes. In this case, the mean temperature, variance, and autocovariance of the temperature measurements change over time due to seasonal fluctuations.
Another example of a non-stationary time series is a stock price series that shows an increasing or decreasing trend over time. In this case, the mean of the series is changing over time, which violates the stationarity assumption.
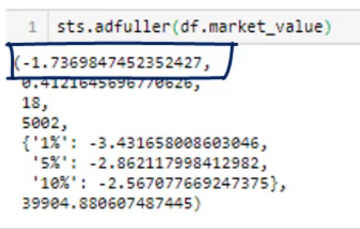
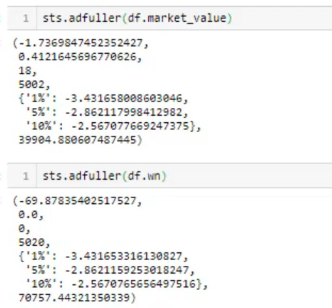





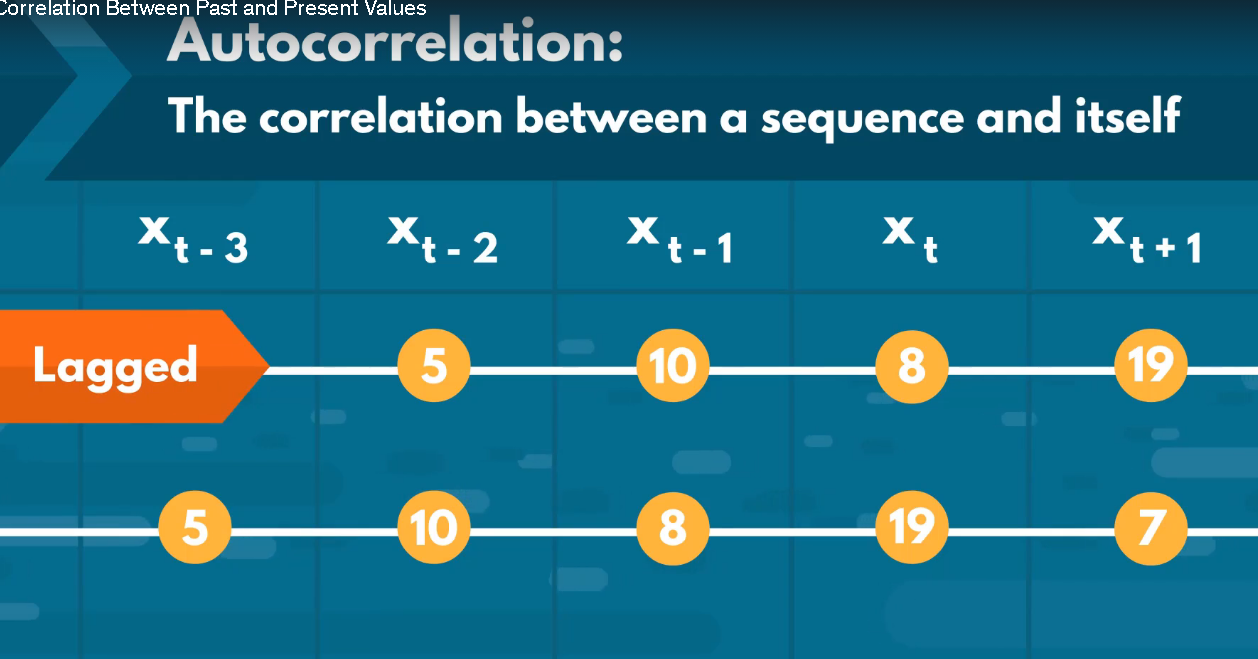
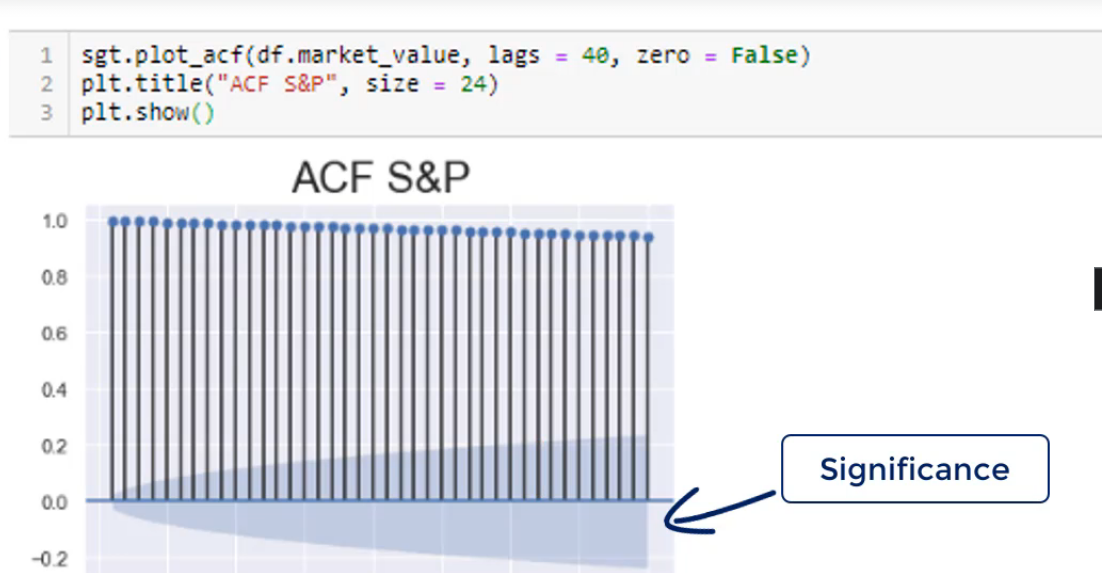
ACF- Autocorrelation

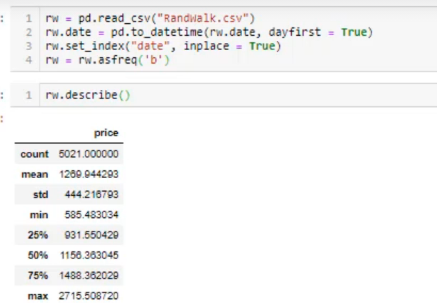
20. Setting the Frequency
